STARTUP REGISTRATION CITIES
- Wrangal
- Nashik
- Navi-mumbai
- Alkleshvar
- Anand
- Barwani
- Bhopal
- Burhanpur
- Chhatarpur
- Chhindwara
- Ahamdabad
- Chennai
- Delhi
- Erode
- Guntur
- Hubli-dharwad
- Indore
- Karur
- Kolkata
- Kurnool
- Madurai
- Mangalore
- Mumbai
- Mysore
- Nizamabad
- Pune
- Rajkot
- Salem
- Thane
- Vadodara
- Vellore
- Vijayawada
- Visakhapatnam
- Surat
- Ahemdabad
- Ahmedabad
- Banglore
- Hubali-dharwar
- Hyderabad
- Jaipur
- Jodhpur
- Mandideep
- Nagpur
- Nilgiris
- Panchmahal
- Patan
- Perambalur
- Porbandar
- Proddatur
- Pudukkottai
- Raichur
- Raipur
- Rajahmundry
- Ramagundam
- Ramanathapuram
- Ratlam
- Robertson-pet
- Sagar
- Sangli
- Satara
- Satna-rewa
- Shimoga
- Services-in-shivpuri
- Surendranagar
- Thanjavur
- Theni
- Thiruvallur
- Thiruvarur
- Thoothukkudi
- Tiruchirappalli
- Tirunelveli
- Tirupati
- Tiruppur
- Tiruvannamalai
- Tumkur
- Udaipur
- Udupi
- Ujjain
- Valsad
- Vapi
- Veraval
- Vidisha
- Viluppuram
- Virudhunagar
- Vizianagaram
- Warangal
Startup Registration Process Anand
Anand is famous for AMUL industries and Dairy industries also established the famous automobile project NANO of TATA . we have our office at Mumbai & Jaipur where we deals in whole state of the Gujrat .
Startup Registration Eligibility & Govt. of India Schemes in Ahmedabad
Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the ambitious ‘Startup India’ Movement to boost digital entrepreneurship at the grassroots level. He spelt out the various salient features of the action plan ..
In a major announcement, he said there will be income tax exemption to startups for the first three years. He also promised faster patent registrations and quicker exits for companies. norms will be relaxed for public procurement of startups-
Important Schemes of the Start-up-
- Startup Intellectual Property Protection (SIPP)
- Provide financial assistance to protect Patent , Trade Marks
- Atal Innovation Mission (AIM)
- Establishment of incubators to nourish
- Entrepreneurship promotion through Self-Employment and Talent Utilization (SETU)
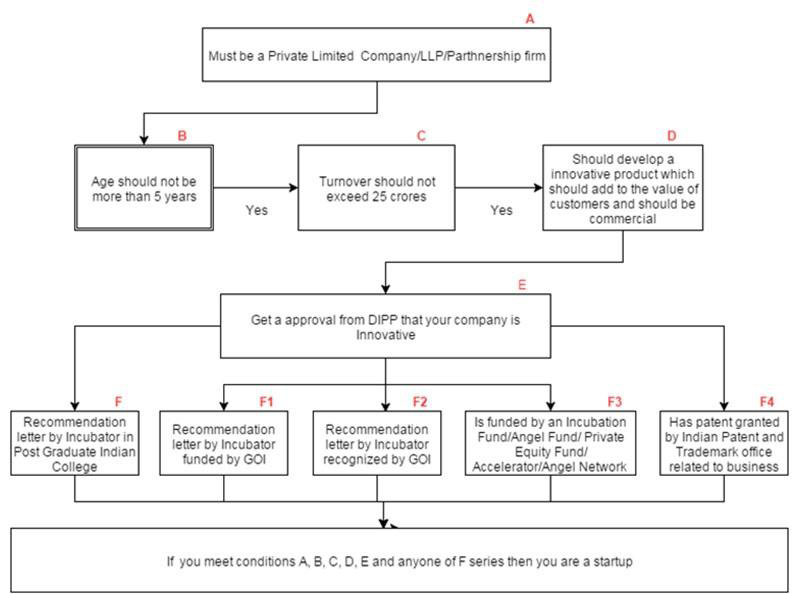
Eligibility for Start-up Registration
1.It must be an entity registered/incorporated as:-
- Limited Liability Partnership – Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008- LLP.
- Registered Partnership firm -Partnership Act, 1932; or
- Private Limited Company under the Companies Act.
2.Five years must not have elapsed from the date of incorporation /registration.
3.Annual turnover (as defined in the Companies Act, 2013) in any preceding financial year must not exceed Rs. 25 crore
4.Startup must be working towards innovation, development, deployment or commercialisation of new products, processes or services driven by technology or intellectual property.
5.The Start-up must aim to develop and commercialise:-
- a new product or service or process; or
- a significantly improved existing product or service.
6.The Start-up must not merely be engaged in:-
- Developing products or services or processes which do not have potential for commercialisation or
- undifferentiated products or services or processes; or
- products or services or processes with no or limited incremental value for customers or workflow
- The Start-up must not be formed by splitting up, or reconstruction, of a business already in existence.
7.The Startup has obtained certification from the Inter-Ministerial Board, setup by DIPP ( Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion ) to validate the innovative nature of the business, and : –
- be supported by a recommendation (with regard to innovative nature of business), in a format specified by DIPP, from an incubator established in a PG college in India; or
- be supported by an incubator which is funded (in relation to the project) from GoI or
- be supported by a recommendation (with regard to innovative nature of business), in a format specified by DIPP, from an incubator recognized by GoI; or
- be funded by an Incubation Fund/Angel Fund/Private Equity Fund/Accelerator/Angel Network duly registered with SEBI that endorses innovative nature of the business; or
- be funded by the Government of India as part of any specified scheme to promote innovation; or
- have a Patent granted by the Indian Patent in areas affiliated with the nature.
Process flow to get Registration of Start-up under Govt. of India
Key Point of Start-ups
- Self Certification Complacencies
- Relaxation in Labour & Environmental Laws .
- Providing Funding Support through a Fund of Funds with a Corpus of INR 10,000 cr .
Tax Exemption
- Start-up Intellectual Property Protection (SIPP)
- Single Window clearance even through Mobile App.
- Innovation Hubs under Atal Innovation mission
- School Innovation Program – 5 lakh School /10 lakh Student .
- Faster Exit for Start-ups
Single Window clearance even through Mobile App
- To serve as the single platform for Startups for interacting with Government and Regulatory Institutions for all business needs & info exchange
- In order to commence operations, Startups require registration with relevant regulatory authorities.
- a checklist of required licenses covering labour licensing, environmental clearances etc. be made available on portal.
Start-up Intellectual Property Protection (SIPP)
- Appointment of Facilitator –Govt. of India has appointed Facilitator to help startup for –
- Patent – for Drafting , filling , handling all matter to protect the Patents and Inventions of the new start-ups in India .
- Trade Mark – for Drafting , filling , handling all matter to protect the trade marks and brand names .
- Fees of the facilitator and Govt filling fee reimburse by the Govt. of India.
- Subsidy up to 80 % – For Patent and Trade mark – subsidy up to 80 % is granted by the Govt. of India to protect trade mark & Patent filed by the Start-ups to protect the IPR’s of the Start-ups for any number of IPR .
- This project is for one year as pilot basis only.
Tax Exemption
- Exemption From Capital Gains Tax-
- Currently investments by venture capital Funds in startup are exempt from this law.
- Income tax exemption to startups announced for 3 years.
- startup initiatives are exempted from income-tax for a period of 3 year. This fiscal exemption shall facilited growth of business and meet the working capital requirements during the initial years of operations.
- Tax exemption on investments above fair market value.
Providing Funding Support through a Fund of Funds with a Corpus of INR 10,000 cr
Relaxation in Labour and Environmental Laws
Objective of compliance remine based on self certification is to reduce the regulatory burden-
Labour laws
- The Building and Other Construction Workers (Regulation of Employment & conditions of Service ) Act. 1996
- The Inter-state Migrant workmen (Regulation of employment & conditions of Service ) Act . 1979
- The payment of Gratuity Act. 1972
- The Contract Labour (Regulation and Abolition ) Act.1970
- The Employees Providen funds and Miscellancous Provision Act. 1952
- The Employees state Insurance Act. 1948.
Environment Laws
- The Water (prevention & Control Of Pollution ) Act.1974
- The Water (prevention & Control Of Pollution ) Cess (Amendment) Act. 2003
- The Air (prevention & Control Of Pollution ) Act. 1981
Innovation Hubs- Atal Innovation mission (AIM)
- Self-Employment and Talent Utilization (SETU) –
- Innovation promotion: to provide a platform where innovative ideas are generated.
- Setting up of 35 new incubators in institutions.
- set up scale up 31 centres.
- Setting-up 13 startup centers Annual funding supports of INR 50 lakhs (shared 50-50by DS and MHRD) shall be provided for three years.
- Setting-up scaling-up 18 Technology business incubators (TBIs ) at NITs IITs/IIMS ect.
- Promote entrepreneurship in biotechnology.
- Five new bio cluters. 50 new bio incubators. 150 technology transfer officer and 20 boi connect offices will be established.
School Innovation Program – 5 lakh School /10 lakh Student
- Innovation core programs for students in 5 lakh schools.
- NIDHI : National initiated for Developing and Hamessing Innovations , instituted through Innovation and Entrepreneurship Development Centers (IEDCs) to support and award INR 10 lakhs to 20 student innovations from IEDSc.
- Uchhattar Avishkar yojana: A joint MHRD-DST scheme whice has carmarked INR 250 crore per annum .The funding towards this research will be 50% contribution from MHRD. 25% from DST and 25% from industry .